The specifications on this page show how we typically install permeable paving for a variety of applications. But every job is different – so if you have any questions or just want to know more, then get in touch today!
For more information, browse our Knowledge Base filled with insights on permeable paving and landscape construction in the form of short, easy-to-read articles.
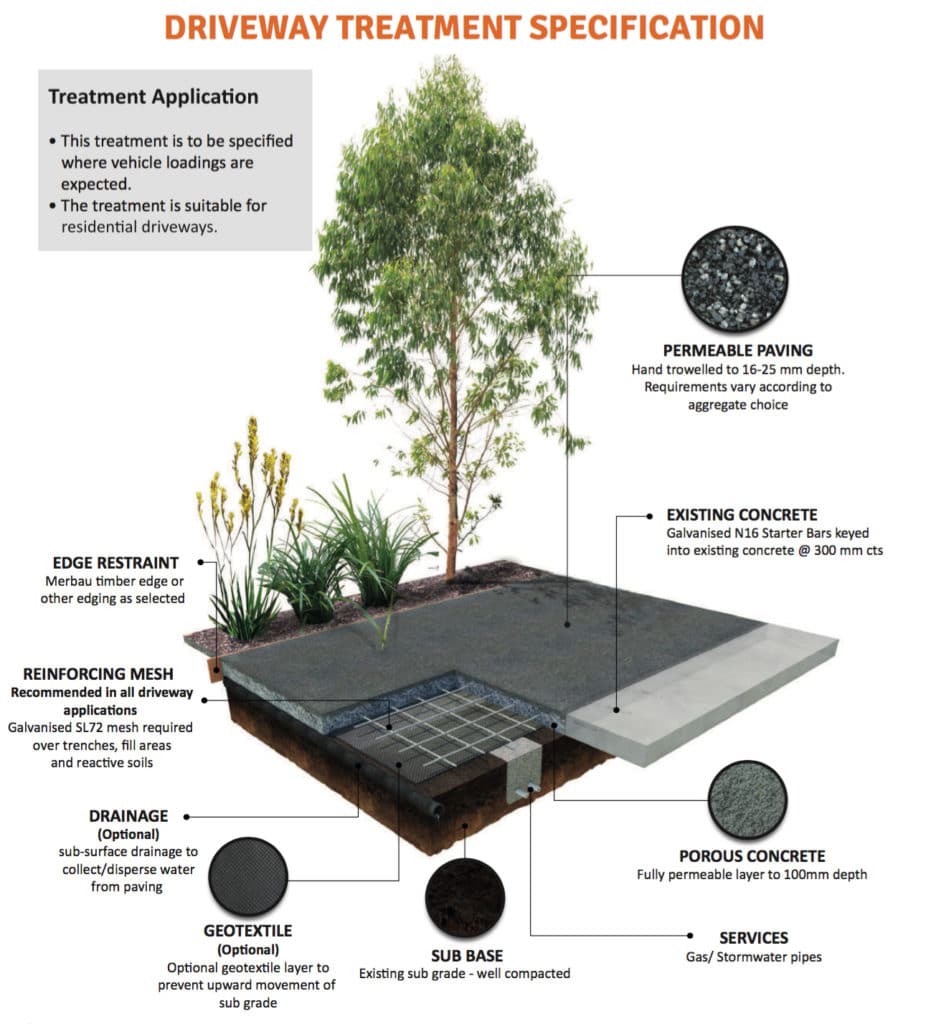
Domestic Grade Permeable Paving
This permeable paving specification is for domestic driveways and pathways. It’s designed and reinforced to tolerate domestic vehicular loadings.
An edge restraint is always recommended for permeable paving installations. Any standard landscaping edge including timber, aluminium, steel or pavers can be utilised.
The reinforced permeable concrete base can be reinforced into adjacent concrete slabs with standard concrete reinforcing designs and techniques.
Galvanised SL72 reinforcing steel is recommended in ALL applications.
For areas within tree protection zones with exposed tree roots, see also the Mature Tree Treatment below.
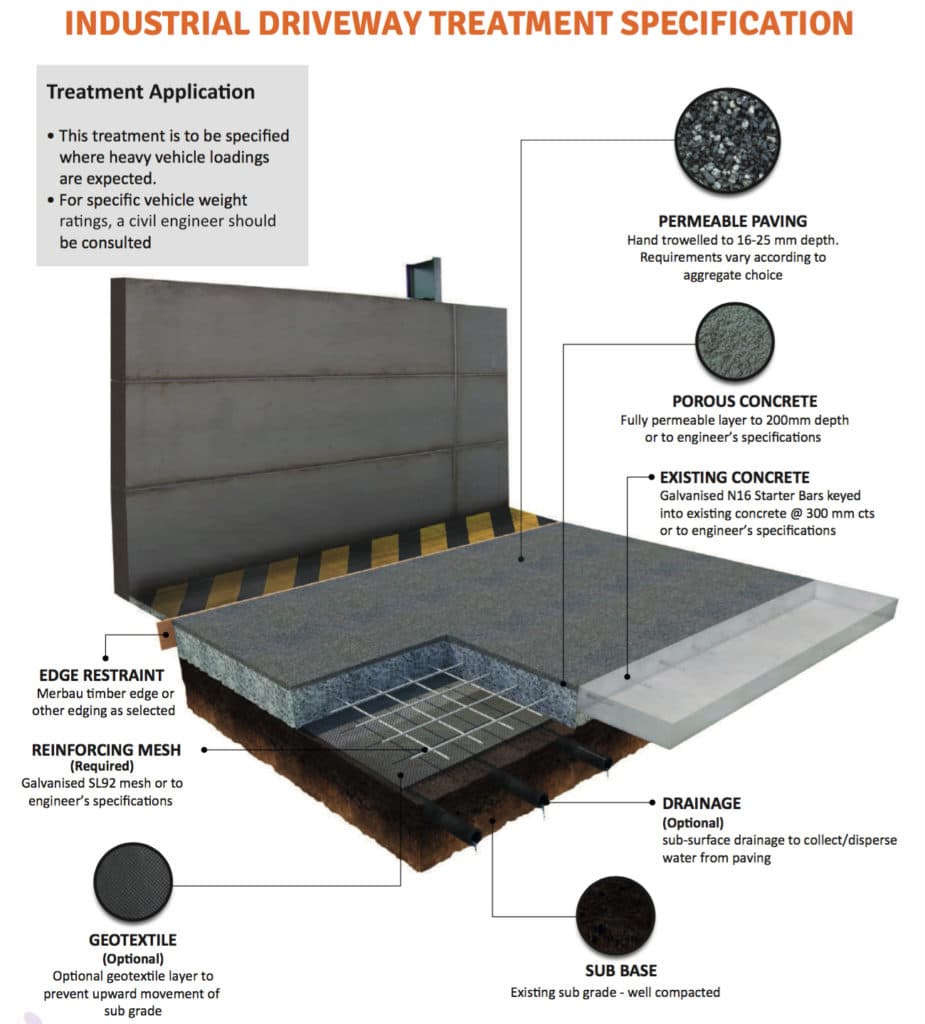
Commercial Rated Permeable Paving
This permeable paving specification is designed for commercial and industrial areas where heavy traffic is expected.
This permeable paving is suitable for commercial carparks, access ways and roads.
The permeable concrete base is thickened to a minimum of 200 mm, and a higher grade (SL92) of galvanised reinforcing steel.
For areas within tree protection zones with exposed tree roots, see also the Mature Tree Treatment below.
Please note: for site-specific vehicle weight loadings, a structural engineer should be consulted.
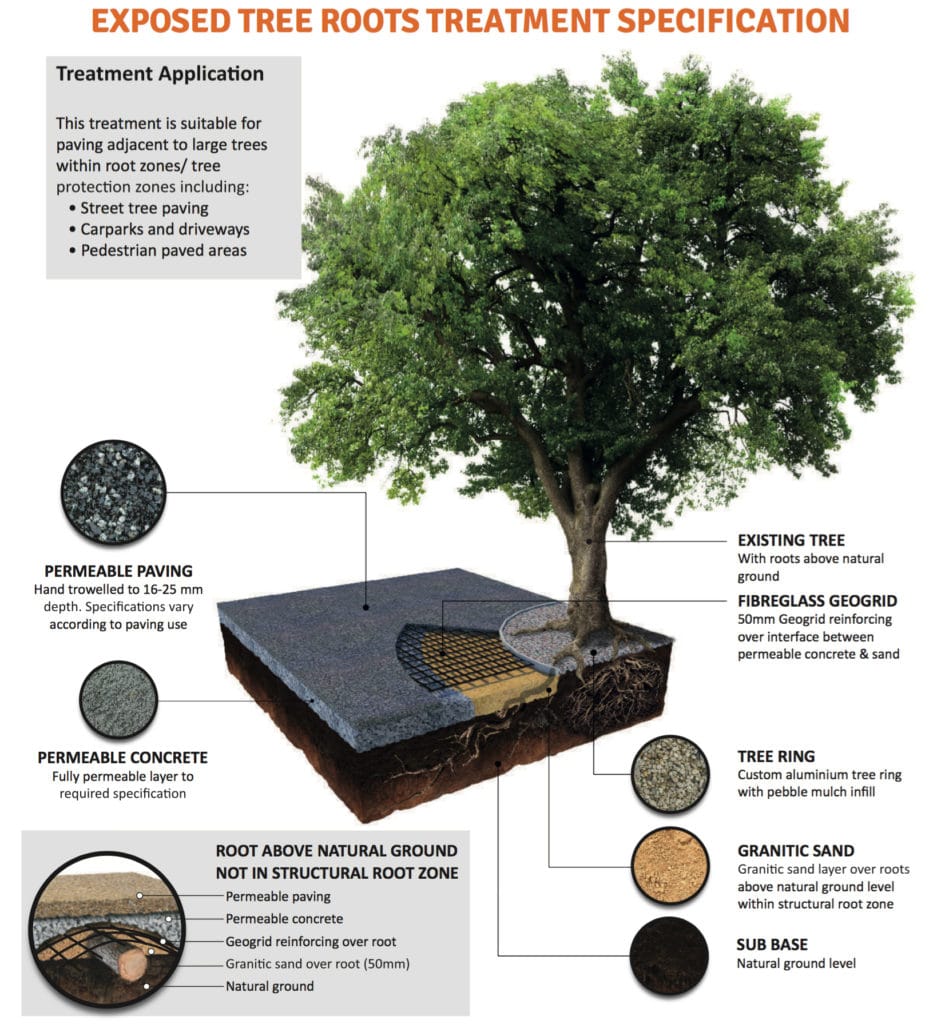
Mature Tree Treatment
This permeable paving specification is designed for paving installations within tree protection zones (TPZs).
In the TPZ where there are generally few exposed tree roots, a standard permeable concrete base is utilised. (For concrete specifications, refer above to either the domestic or commercial specifications).
Any raised tree roots outside of the structural/critical root zone are bedded in granitic sand, and stabilised with Geogrid fibreglass reinforcing mesh.
Within the structural/critical rootzone and once raised tree roots are encountered, granitic sand is used for the paving base. Inclusion of Geogrid reinforcing within the permeable paving enhances flexibility and tolerance of root movements.
For tree surrounds within footpaths, streetscapes and carparks, refer to the two Tree Surround Specifications below.
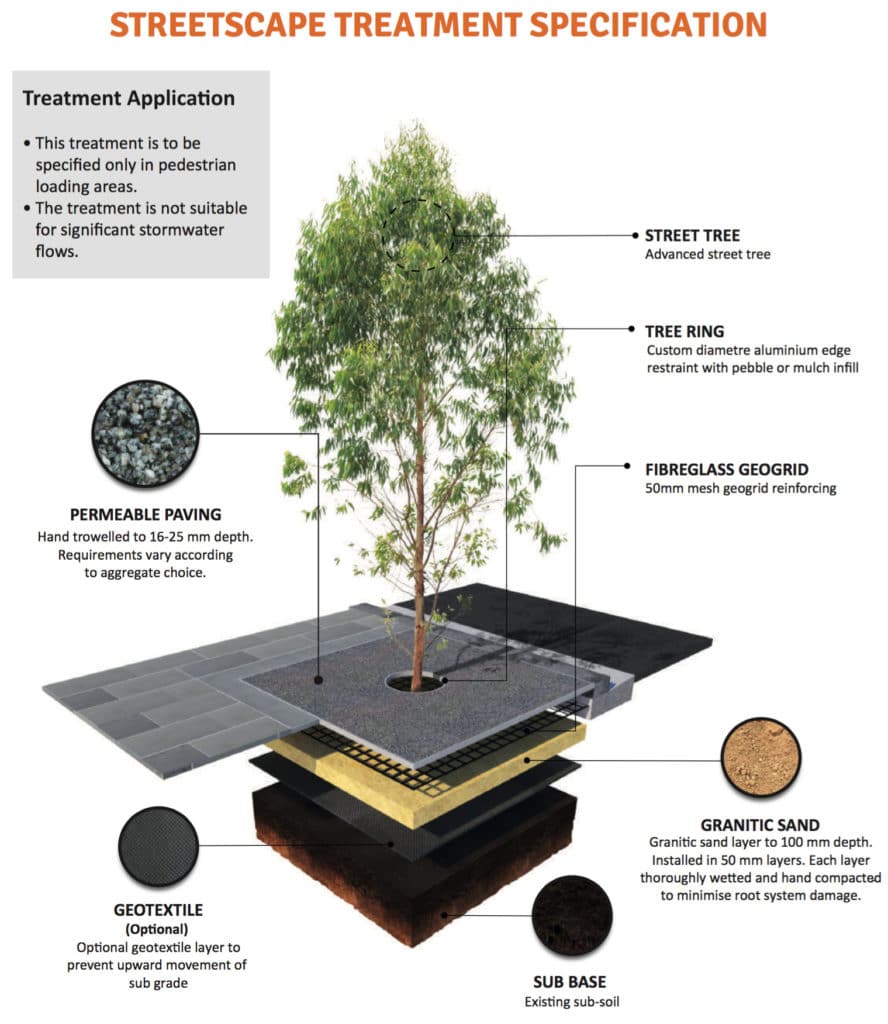
Streetscape Tree Surround
This permeable paving specification is designed for tree surrounds in pavements/pedestrian areas only.
Granitic sand is used as a base, and Geogrid fibreglass reinforcing is added to the paving to enhance flexibility and stabilise the paving during movement due to tree growth.
This treatment is not recommended for vehicular loadings, nor for areas where high permeability is required – e.g. should the pavement be draining water into the tree surround.
For high permeability tree surrounds suitable for vehicular loadings, refer to the Car Park Tree Surround specification below.
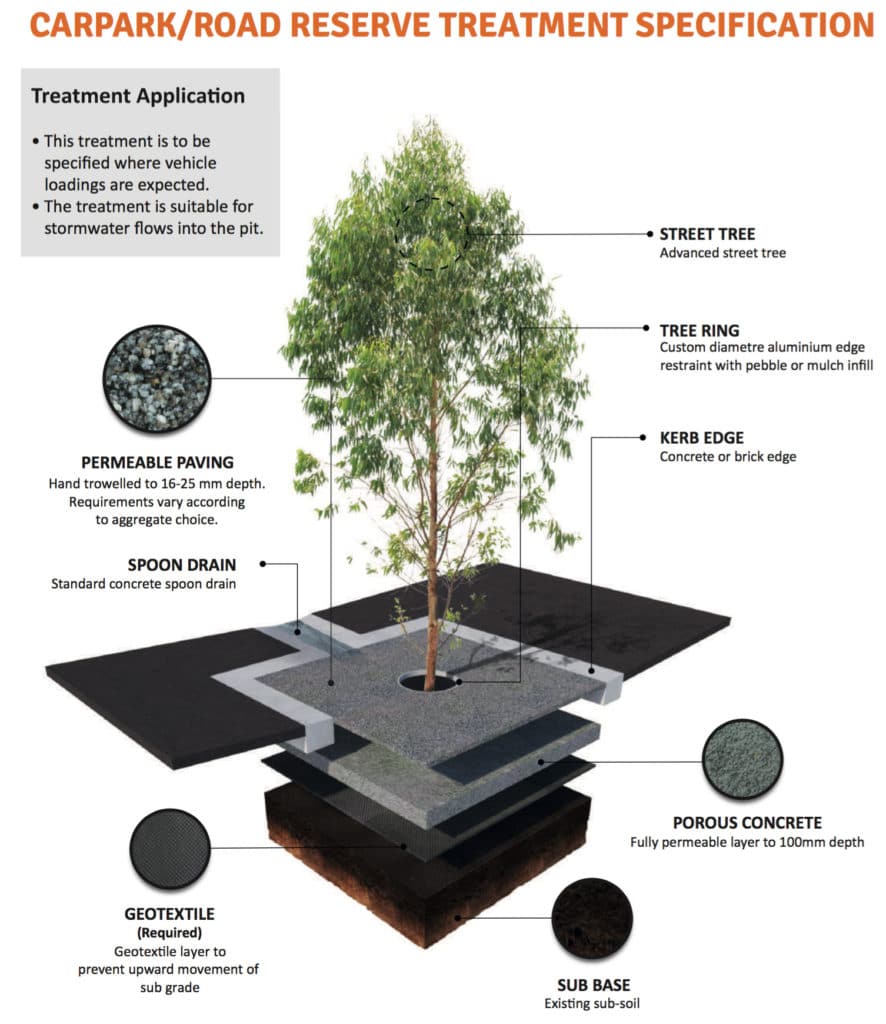
Car Park Tree Surround
This permeable paving specification is designed for tree surrounds in carparks and other areas with occasional vehicular traffic.
The higher permeability of porous concrete vs. granitic sand makes it suitable for areas where large amounts of water will be directed into the pit as part of a Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) strategy.
The porous concrete base is installed for maximum permeability and strength. Geotextile fabric should also be installed under the porous concrete to prevent the upwards migration of fines from the subsoil during heavy rain events when large amounts of water enter the tree surround.
Concrete Resurfacing
Pebble Pave permeable paving can also be used for concrete resurfacing.
The paving is reinforced over any cracking with Geogrid reinforcing mesh.
An aluminium edge restraint is applied to the edges, and the existing concrete ground down to enable a flush transition between the new finished surface and any existing hard surfaces such as the footpath or garage slab.
For more information, see the Driveway Resurfacing page.